
It’s particularly useful when assessing the short-term financial health of potential investment opportunities. This ratio, however, should not be viewed in isolation but rather as part of a holistic financial analysis. While a high Current Ratio is generally positive, an excessively high ratio may indicate underutilized assets. It’s essential to consider industry norms and the company’s part time work home bookkeeper jobs employment specific circumstances. For example, in some industries, like technology, companies may maintain lower Current Ratios as their assets are less liquid but still maintain financial health. If a company has $500,000 in current assets and $250,000 in current liabilities, its Current Ratio is 2 ($500,000 / $250,000), indicating that it has twice the assets to cover its immediate obligations.
Decrease In Current Assets – Common Reasons for a Decrease in a Company’s Current Ratio
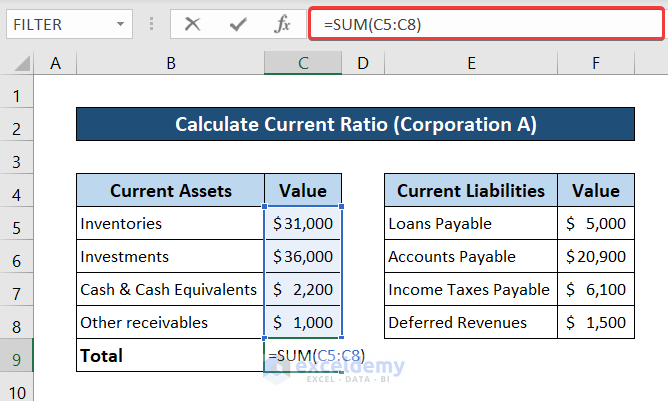
Let’s look at some examples of companies with high and low current ratios. You can find these numbers on a company’s balance sheet under total current assets and total current liabilities. Some finance sites also give you the ratio in a list with other common financials, such as valuation, profitability and capitalization. The current ratio is a metric used by accountants and finance professionals to understand a company’s financial health at any given moment. This ratio works by comparing a company’s current assets (assets that are easily converted to cash) to current liabilities (money owed to lenders and clients). A more conservative measure of liquidity is the quick ratio — also known as the acid-test ratio — which compares cash and cash equivalents only, to current liabilities.
Advanced ratios
One limitation of the current ratio emerges when using it to compare different companies with one another. Businesses differ substantially among industries; comparing the current ratios of companies across different industries may not lead to productive insight. If all current liabilities of Apple had been immediately due at the end of 2021, the company could have paid all of its bills without leveraging long-term assets.
Table of Contents
- However, if you learned this skill through other means, such as coursework or on your own, your cover letter is a great place to go into more detail.
- The current ratio can be useful for judging companies with massive inventory back stock because that will boost their scores.
- Managers should also monitor liquidity and solvency, and there are three additional ratios that can help you get the job done.
The current ratio also sheds light on the overall debt burden of the company. If a company is weighted down with a current debt, its cash flow will suffer. In this case, current liabilities are expressed as 1 and current assets are expressed as whatever proportionate figure they come to.
To manage cash effectively, you need to monitor several other short-term liquidity ratios. The balance sheet differs from an income statement, which reports revenue and expenses for a specific period of time. The cash flow statement reports the cash inflows and cash outflows for a month or year. It’s ideal to use several metrics, such as the quick and current ratios, profit margins, and historical trends, to get a clear picture of a company’s status.
How Does the Industry in Which a Company Operates Affect Its Current Ratio?
The current ratio can also provide insight into a company’s growth opportunities. A high current ratio may indicate that a company has excess cash that can be used to invest in future growth opportunities. In contrast, a low current ratio may indicate that a company needs to improve its liquidity before pursuing growth opportunities. Investors and stakeholders can use the current ratio to make investment decisions. A company with a high current ratio may be considered a safer investment than one with a low current ratio, as it can better meet its short-term debt obligations.
For example, a company may have a very high current ratio, but its accounts receivable may be very aged, perhaps because its customers pay slowly, which may be hidden in the current ratio. Analysts also must consider the quality of a company’s other assets vs. its obligations. If the inventory is unable to be sold, the current ratio may still look acceptable at one point in time, even though the company may be headed for default. Managers who take a measure of a company’s turnover ratios can increase liquidity, and produce a high current ratio. If current asset or current liability balances change, so too will the company’s current ratio. However, if you learned this skill through other means, such as coursework or on your own, your cover letter is a great place to go into more detail.
However, a current ratio of greater than 1 provides additional cushion against unforeseeable contingencies that may arise in the short term. Both of these current accounts are stated separately from their respective long-term accounts on the balance sheet. This presentation gives investors and creditors more information to analyze about the company. Current assets and liabilities are always stated first on financial statements and then followed by long-term assets and liabilities. Current liabilities are best paid with current assets like cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities because these assets can be converted into cash much quicker than fixed assets.















